Attribution Methodology
There are two distinct ways of attributing sales to marketing effort: based on tracking and based on uplift estimation.

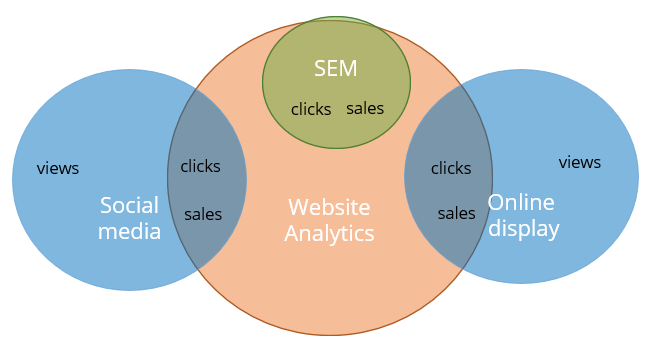
Touch attribution links each sale with the ads that the customer clicked on or viewed and is mostly used for online advertising. Offline, it is used for direct response campaigns.
Uplift estimation at the most basic level is running a test campaign and comparing the level of sales without marketing (baseline) with sales when marketing is on.
Since separate testing is impractical for every parameter of real-life campaigns, the more complex sophisticated version statistically correlates desired outcomes, such as sales, website visits, new customers, with marketing inputs such as advertising, reporting on additional outcomes generated by each extra unit of inputs. This method is called marketing mix modelling (MMM) and it is the main evaluation method within InContekst.
Touch attribution is widely used by advertising platforms, including Google Ads and Facebook Ads, and website analytics, notably Google Analytics (GA4).
Advertising platforms use it report on Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) and optimise campaigns. However, their reporting only takes into account the ads run on those platforms. Website analytics can string together the entire history of customer interactions, however it does not credit the ads that the customer viewed but not clicked-through on.
Advantages of touch attribution are its simplicity for the end user and rich information it can provide in a short amount of time.
Disadvantages are apparent when you use multiple platforms. Each ad platform credits all the sales to its own advertising only; in extreme cases the total amount credits exceeds total sales!
And while automatic optimisation shows the the ads to people who are more likely to buy, this doesn't mean that those ads influenced people's buying decisions. It will happily claim credit for the purchases that would have happened anyway, wasting your budget.
Tracking across devices is also problematic, even if all of your marketing is digital. The customer could view a Facebook ad on their phone or a Youtube ad on smart TV but use a computer to make a purchase. This leads to inconsistent assessment, as some sales will be correctly attributed and others won't.
Uplift estimation works by comparing the level of sales without marketing (baseline) with sales when marketing is on, as shown below in a vastly simplified form:
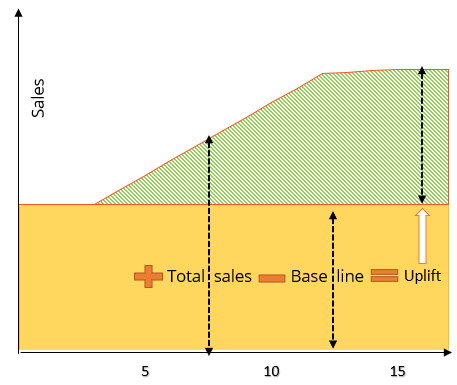
The most basic form of uplift estimation is running a test campaign and applying the learnings to the ongoing one. Test campaigns are considered gold standard for ensuring marketing really attracts new customers and influences sales. However, you cannot afford to run a separate campaign for each channel, message, and format that you wish to test. You also cannot interrupt your ongoing marketing efforts for tests.
MMM correlates variations in target metric, such as sales revenue, with the levels of different marketing activities. The calculation reports that for each additional unit of input (e.g., dollar spent or impression generated), the target outcome increases by a certain amount, which is essentially the effectiveness of that input.
MMM could be used to build robust models revealing long-term relationships that could be used for forecasting future sales and planning campaigns. Such models take into account promotion on various channels, price, competitors activity, environment (e.g. weather, interest rates). They typically use weekly data (because the purchase cycle is usually a week) and require 100+ datapoints, i.e., about 2 years worth of data.
When you need the results sooner, the options are to to reduce accuracy, i.e., only using the results for understanding the current performance and immediate adjustments, rather than long-term planning, to use daily, rather than weekly, cycle, for example, measuring web traffic generated by marketing, or to split the data by geographical area to obtain more datapoints. When used in combination, these measures allow collecting the required amount of data in about a week.
Advantages of MMM:
However, MMM requires planning, careful data collection and preparation, which are part of InContekst automation.
Marketing Mix Modelling - the math behind MMM and detailed capabilities description.